Debasish Biswas
Jadavpur University, India
Title: Observing giant room temperature magneto dielectric response in silica-based oxide nano glass
Biography
Biography: Debasish Biswas
Abstract
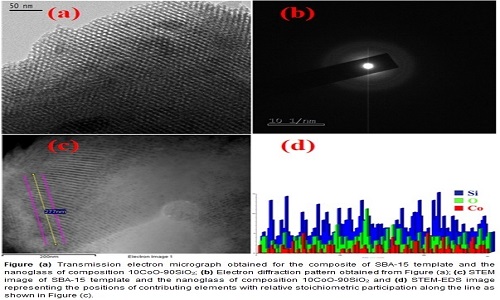
Nano dimensional silica-based glasses of compositions xCoO-(1-x)SiO2 with x having values 10 and 30 were synthesized by a sol-gel method within the nanopores of mesoporous template. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopic (XPS) analysis showed the presence of Co2+ and Co3+ species in the glasses causing electronic conduction in this amorphous system. At room temperature the resistivity values exhibited by the nano glasses were nearly three orders of magnitude lower than those of the corresponding bulk glasses. The resistivity data for the nano glasses on analysis confirmed the conduction to arise due to small polaron hopping between the localized states represented by those ions. Typical values of inter-site separation distance extracted from the said analysis were found to be ~7 Å. The values of magneto dielectric parameter for the different nanocomposites were large with the highest value found to be in the range 500% to 45% for the frequencies 1 kHz and 1 MHz respectively for a nanocomposite with glass composition of 30CoO-70SiO2. The results were then fitted to Catalon’s model based on two dielectrics in series with different resistivity values. The satisfactory fit of the measured data to the theoretical model based on a negative magneto resistance of the nano glasses indicate that an enhancement of spin polarized electron hopping caused this effect. The magnetization change as a function of the applied magnetic field was calculated for the nanocomposites. The super exchange interaction between Co2+ and Co3+ ions through the intervening oxygen ions gave rise to the ferromagnetic like behaviour of the samples. In future these materials may be used as good magnetic sensors.