Thieo E Hogen Esch
University of Southern California, USA
Title: Nano-scale membranes based on polystyrene sulfonic acid blends
Biography
Biography: Thieo E Hogen Esch
Abstract
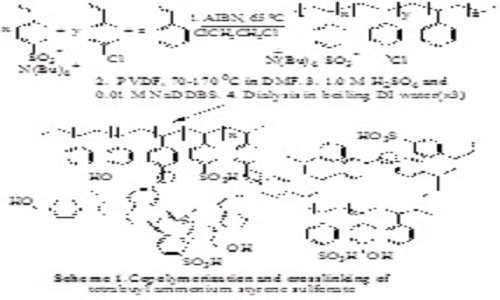
Flexible, strong, colorless and transparent polyvinylidenefluoride-olystyrenesulfonic acid (PVDF-PSSA) proton exchange membranes1-3 were synthesized by first mixing DMF solutions of PVDF and tetrabutylammonium polystyrenesulfonate (PTBASS) terpolymer having smaller (<20%) mole fractions of styrene (S) and 4-chloromethylstyrene (CMS). The tetrabutylammonium styrene (BASS) sulfonate precursor monomer was synthesized through simple ion exchange of sodium styrene sulfonate and tetrabutylammonium-chloride or bromide. The PBASS terpolymer precursor was synthesized through a conventional radical copolymerization of BASS, styrene and CMS. The PVDF-PBASS blends are formed by dissolution of the two polymers in DMF, followed by evaporation and thermal cross-linking through annealing at about 170°C. The EAS type crosslinking appears to involve the formation of TBA benzyl sulfonates that may directly benzylate the S and CMS units of the terpolymer. The PVDF-PBASS blends are optically transparent above about 165°C and remain so after rapid cooling followed by ion exchange mediated by a mixture of 1.0 M H2SO4 and surfactants and repeated aqueous dialysis giving low (<40 wt%) water content PVDF-PSSA membranes.4 Transmission electron microscopy confirms the presence of small (≥5 nm) PSSA domains the size and nature of which is still unknown. The water uptake, proton conductivity, ion exchange capacity (IEC), and methanol permeability of the membranes are tunable through variation of the PVDF/PSSA content and the sulfonic acid content of the terpolymer. At higher PSSA contents (>20 wt.%) the membranes were shown to have proton conductivities comparable or higher than Nafion-117 but significantly lower methanol permeabilities. These low cost, environmentally appealing and conveniently accessible membranes can be used in direct methanol fuel cells (DMFCs) and other applications.