Sungsoo Kim
Pai Chai University, Korea
Title: Synthesis and characterization of ultra-thin and ultra-highly conductive poly(3,4- ethylenedioxythiophene) nanofilm
Biography
Biography: Sungsoo Kim
Abstract
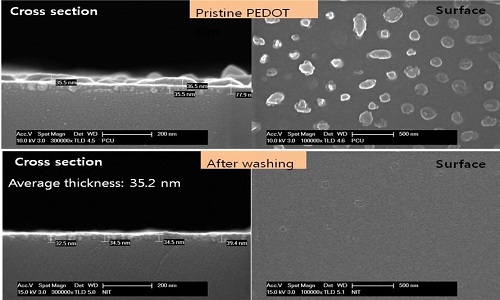
Poly-3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene (PEDOT) is a very versatile and highly conductive polymer reported up to ca. 4,500 S/cm so far. In this study, PEDOT with an ultra-high conductivity of about 6,000 S/cm and an ultra-thin film of about 35 nm is presented. The PEDOT was processed via an oxidative chemical vapor phase polymerization method (VPP). Glass and PET surfaces were covered with ferric chloride (FeCl3) oxidizing agent mixed with polyurethane diol (DUDO) and poly(ethylene glycol–propylene glycol–ethylene glycol) (PEG-PPG-PEG) prior to their exposure to 3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene (EDOT) vapors. Optical microscope images show that the precursor film (oxidant mixture) covered on wafer or PET has very smooth and uniform surface. FE-SEM and AFM results revealed that PEDOT film after washing with n-butanol is very smooth, thin, and homogeneous (RMS is lower than 3 nm). Ultra-thin PEDOT films were further characterized by various other tools such as XRD, FT-IR, Raman, XPS, TGA, and so on. All other results obtained by various analyzing tools strongly support that PEDOT is indeed an ultra-highly conductive film far surpassing the most representative transparent electrode such as ITO (indium tin oxide).